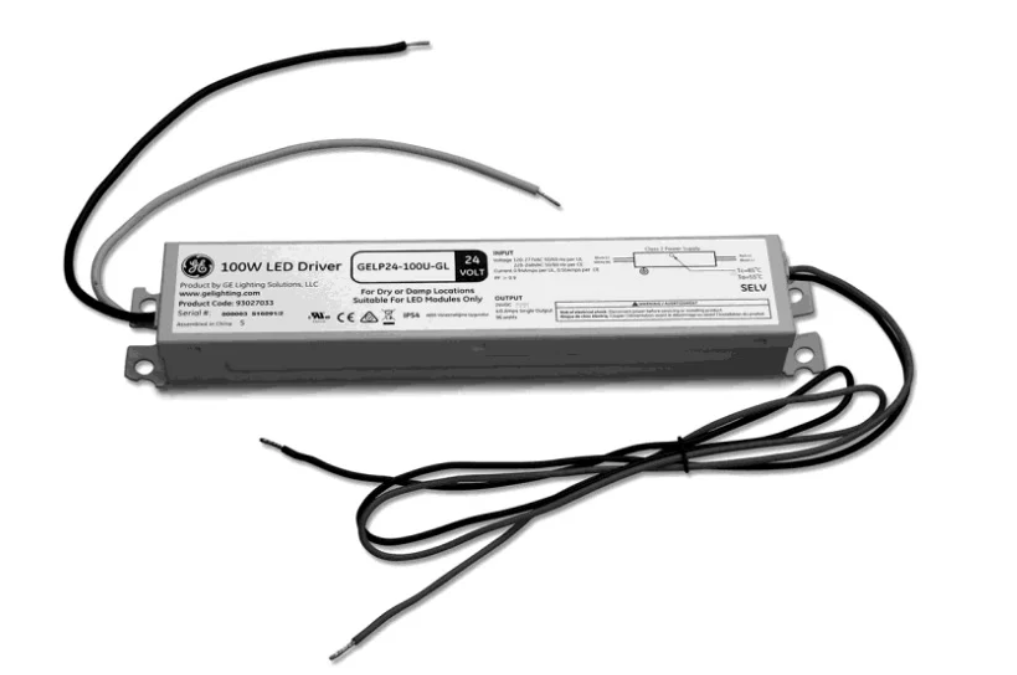
LED technology is a completely different lighting method than other conventional lighting types. For one, LEDs require an LED driver to control the electrical current. The LED driver is a critical component for LED lighting systems, ensuring safe and efficient operation. They often look similar to a fluorescent ballast, but come in all shapes and sizes. Some are even hidden within what you might consider to be the “bulb,” such as an A19 or T8 LED. Internal drivers are commonly used in standard household bulbs for ease of replacement, while external drivers are used in commercial or outdoor lighting applications where separate, replaceable power supplies are needed. Without an LED driver, LEDs may flicker, overheat, or fail prematurely.
Ins & Outs of LED Drivers
Although LED lighting has many great benefits—including energy efficiency, long life, and environmental friendliness—one potential disadvantage is that LEDs require a consistent, constant flow of electrical current at all times, at the exact voltage required. Doing this helps the LEDs stay at a consistent temperature. If an LED runs too hot, it may begin to malfunction and experience poor performance. To help keep LEDs running in top form, this is where an LED driver comes in. LED drivers protect LEDs against voltage spikes, short circuits, flickering, and overheating. They ensure that LEDs function correctly by providing precise power regulation. Click here to shop the selection of LED drivers on ShineRetrofits.com.
If an LED driver fails, it may cause the LED lights to flicker or not light up at all, and LED drivers can have a shorter lifespan than the LED fixtures they power.
What is an LED Driver?
An LED driver is a device that does exactly what it sounds like—it drives the power to one or more LEDs and acts as a power supply for LEDs. As we mentioned previously, a good thing about LEDs is that they are energy efficient—they do not require a large amount of power to get them going. LEDs actually work on DC power at a relatively low voltage—usually between 2V to 4V. Because of that, they require something that will convert input AC voltage into the DC voltage required by LEDs. The importance of input voltage compatibility cannot be overstated, as the LED driver must handle a range of input voltages to ensure stable operation and protect the LEDs from voltage fluctuations. The LED driver acts not only as an electrical current management system, but also as a protective buffer. It’s like Baby Bear in the Goldilocks tale—everything is just right. In addition to being compared to ballasts for fluorescent lights, LED drivers are also similar to transformers, which are other types of power regulation devices.
As you look at the variety of LED driver products out there today, you’ll notice there are two main types (or common types) of LED drivers: constant voltage and constant current. These main types serve different purposes in different situations. There are also non-dimmable LED drivers available, which are suitable for applications where dimming is not required. It’s important to read the product specifications of your LED lamp to make sure you are using the correct type. They are not usable interchangeably. LED drivers typically last between 30,000 and 50,000 hours depending on usage and environmental factors, and they can come in various shapes, including round and rectangular, to fit different fixtures.
Constant Voltage LED Driver
A constant voltage driver is used for LED products that require a steady and constant DC output voltage to keep them performing well. These drivers provide a stable output voltage and supply a maximum output current based on the connected load, ensuring that the necessary power is supplied to the LEDs. Many times, a constant voltage driver will be used with an LED lamp or other product that has a built-in driver for the current already installed. All it really needs is something to keep the voltage consistent. Constant voltage drivers are commonly used for LED strips, where it is important to match the output current of the driver to the current requirements of the LED strips to ensure proper functionality and performance. It is also mainly for applications where the LEDs are in a strip configuration and are all in a parallel connection to the driver. It ensures that every LED receives the same amount of voltage from the driver. The driver must be compatible with the specific LED chips and load connected to ensure safe and reliable operation. When selecting an LED driver, choose one with the appropriate IP rating for the environment where it will be used, and evaluate its efficiency by looking for a high power factor and low energy loss. LEDs often use constant voltage drivers for illuminating landscape and accent lighting, back-lighting for advertising signs, and huge high-definition LED displays. Usually, they are available in a number of different wattages and can also come with dimming capabilities.
Constant Current LED Driver
Rather than regulating the voltage, a constant current LED driver manages the actual current that is supplied to the LED’s diode, which is required for the p-n junction. This type of driver is especially important when driving an LED array, as it ensures that the current supplied is proportional to the light output of the LEDs. Additionally, constant current drivers can adjust the output current to match the current requirements of the connected LEDs, providing precise current regulation for optimal performance and longevity. This regulation is crucial because LEDs have a negative temperature coefficient, meaning their resistance drops as they heat up, so careful current regulation is needed to avoid thermal runaway. Too much of this forward current can potentially overheat the LED, causing it to malfunction. A constant current driver is primarily for situations where an LED lamp does not already have a current driver built in. It keeps a consistent current running through a string or series of LEDs. If the LED driver fails to maintain optimal operation, it may need to be replaced to ensure continued safe and efficient performance. Constant current drivers are available in a variety of different configurations.
LED Configurations
A key piece of understanding how LED drivers work is knowing the different LED configurations. The two most common LED configurations are series and parallel. In a series configuration, one LED's anode (aka positively charged electrode) is connected to another's cathode (aka negatively charged electrode). This enables a single, continuous current to flow through all the LEDs in the series, usually called a string. Important to note: in order to keep the entire string of LEDs running, you have to make sure you’re providing enough voltage for the sum of them all. So, for instance, if each LED needs 2V to illuminate and you have 10 LEDs, they will require 20V.
Another standard configuration for LEDs is a parallel configuration. Here, we would connect multiple strings of LEDs in parallel—or side-by-side—to a driver. So, for instance, if you had 50 LEDs you could have five strings of 10 LEDs each running in parallel, rather than all 50 in one string. A parallel configuration is for situations where you want to limit the voltage necessary to operate the strings of LEDs. You can also configure parallel strings of LEDs in a matrix. This happens when sets of parallel strings of LEDs connect to each other in a series.
Proper wiring and compliance with electrical safety standards are essential in all LED configurations to ensure safe operation and prevent hazards. LEDs designed for household use typically include internal drivers, making replacement and installation easier for residential applications.
Dimming & Color Sequencing
Depending on their specifications, some LED drivers can also facilitate dimming and/or color sequencing. When considering dimming, it is important to select a compatible dimmable LED driver and ensure it matches the required dimming type, such as TRIAC, 0–10V dimming, trailing edge, or PWM. Dimmable LED drivers often require an external dimmer or other dimming control devices to function properly. For example, TRIAC and trailing edge dimmers are commonly used in building and household systems, while 0–10V dimming is popular for commercial and outdoor lighting applications, especially with IP67-rated LED drivers that are designed for weather-resistant environments.
Depending on the type of LED driver you select, its dimming ability can cover the full range. The driver dims the LEDs by either shortening the amount of leading current going through it, or by a method called pulse width modulation (PWM). Most drivers that offer dimming use PWM. This allows dimming without flickering and with usually very little color change in the LEDs. It is good to note that dimming does not affect an LED’s performance. It also will not have a negative impact on how long it lasts. In fact, dimming can potentially help LEDs last longer as it will reduce the heat it creates when lit.
For safety and electrical code compliance, Class II power supplies are often required, as they adhere to strict standards such as UL, ETL, and IEC 61439-1, ensuring proper insulation and fire hazard prevention. Additionally, emergency backup drivers play a crucial role by providing power to LED fixtures during power outages, ensuring essential lighting remains operational.
With color sequencing or changing, many times an LED string or product may have LEDs of different colors. In fact, many times a “white” colored LED lamp is actually not using “white” colored LEDs. Rather, it uses different colors that, when shown together, produce white light. So with a driver with this capability, you would be able to control the different colors of LEDs in the product to create a full rainbow of colors depending on which are on and which are off. Shop LED Drivers Now
LED Lighting Applications
LED lighting has revolutionized the way we illuminate our homes, businesses, and public spaces, thanks to its remarkable energy efficiency, long lifespan, and adaptability to various applications. In residential environments, LED lights are commonly used for under-cabinet lighting, recessed fixtures, and outdoor landscape lighting, offering homeowners a reliable and efficient way to brighten their spaces. Commercial and industrial facilities also benefit from the superior performance of LEDs, with high-output lighting solutions for warehouses, offices, and retail stores that demand consistent and powerful light output.
The success of these lighting systems relies heavily on the use of constant current LED drivers and constant voltage drivers, ensuring that LEDs operate within safe parameters and deliver optimal brightness. High quality LED drivers are essential for maintaining steady voltage and current, preventing damage to the LEDs and extending their service life. For spaces that require adjustable lighting, dimmable LED drivers make it easy to control brightness levels, creating comfortable and energy-efficient environments tailored to specific needs.
By choosing the right drivers for each application, users can maximize the efficiency of their lighting systems, reduce energy costs, and save money over time. Whether illuminating a cozy living room or a bustling warehouse, the right combination of LEDs and drivers ensures reliable performance, consistent light output, and long-term savings across a wide range of applications.
Environmental Considerations
When designing or upgrading a lighting system, it's important to factor in environmental considerations to ensure both efficiency and safety. One key aspect is the IP rating of an LED driver, which indicates its ability to resist dust and water. For outdoor installations or damp environments, selecting drivers with a higher IP rating is crucial to protect against environmental hazards and maintain reliable operation.
Another important factor is the power factor of the LED driver. High power factor drivers use electricity more efficiently, helping to lower energy costs and reduce the risk of voltage spikes that can damage sensitive electronics. In addition, choosing drivers with built-in protection features can help safeguard the lighting system from electrical surges and ensure stable performance.
For critical areas where uninterrupted lighting is essential, such as emergency exits or safety pathways, emergency LED drivers with battery backup are a smart choice. These drivers automatically provide power during a power outage, ensuring that essential lights remain operational and compliant with safety regulations.
Selecting the most suitable types of LED drivers—whether constant current or constant voltage—based on the specific requirements of the lighting system is vital for achieving optimal performance and energy efficiency. By considering factors like IP rating, power factor, and emergency capabilities, users can create a robust, efficient, and environmentally friendly lighting system that stands up to the demands of any application while minimizing energy costs and environmental impact.